A categorized list of all Java and JVM features since JDK 8 to 21
From Java 8 to 21

Last updated on 2023/09/22 to include changes up to JDK 21.
This article is also available in Chinese by Alex Tan.
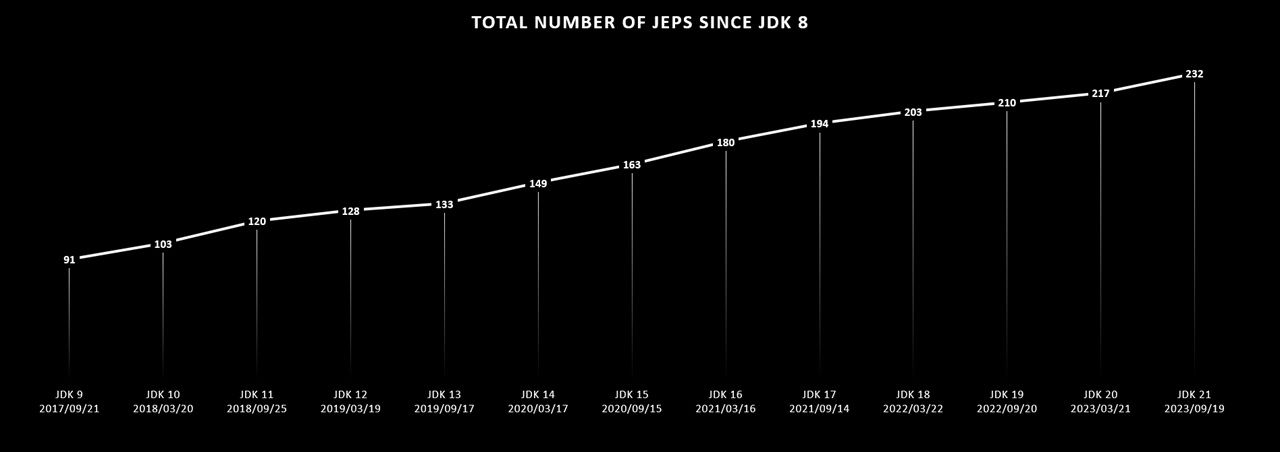
Since the release of version 8, up to version 21, Java is shaped by 232 JDK Enhancement Proposals (JEPs) and many more smaller updates, each of which brings some improvement to the platform. This page is a categorized and curated list of the most important improvements.
Contents of this page:
- New Language Features
- New APIs
- Performance Improvements
- Security Improvements
- Launching
- Packaging
- Javadoc
- Bytecode
- New supported platforms
- New Version Scheme
- Deprecation and removal
The full list of JEPs can be found on the OpenJDK website under the jdk and jdk9 projects.
All features are generally available and enabled by default, except if they are labelled with one of the following:
- Preview 🔍 features are fully specified and implemented, but not yet considered to be final. They are considered to be almost complete, waiting for an additional round of real-world feedback. They have to be explicitly enabled.
- Experimental 💥 features are less stable, and more likely to change. They also have to be explicitly enabled.
- Incubator 🥚 modules are non-final tools and API's, and are distributed in separate modules.
New Language Features
Since Java 8 lots of improvements were made to the language. This section is a quick recap on what happened in the last years. For a more in-depth guide, see New language features since Java 8.
-
Pattern Matching for
switchsupporting type patterns and guarded patterns
JDK 21(Preview 🔍 in JDK 20JDK 19JDK 18JDK 17)String formatted = switch (o) { case Integer i when i > 10 -> String.format("a large Integer %d", i); case Integer i -> String.format("a small Integer %d", i); case Long l -> String.format("a Long %d", l); default -> o.toString(); };→ Related: Inside Java Podcast Episode 17 “Pattern Matching for switch” with Gavin Bierman
→ Inside Java Podcast Episode 26: “Java 19 is Here!” with Brian Goetz and Ron Pressler
→ Inside Java Podcast Episode 28: “Java Language - State of the Union” with Gavin Bierman -
Record Patterns for
switchandinstanceofto deconstruct complex nested structures
JDK 21(Preview in JDK 20JDK 19)if (r instanceof ColoredPoint(Point2D(int x, int y), Color c)) { // work with x, y, and c } -
Unnamed Variables (Preview 🔍)
JDK 21var _ = mySet.add(x); // ignore the return value try { // ... } catch (Exception _) { // ignore the exception object // ... } list.stream() .map((_) -> /* ... */) // ignore the parameter .toList(); -
Unnamed Patterns (Preview 🔍)
JDK 21if (r instanceof Point(int x, _)) { // work with x, ignore second parameter } -
String Templates - extensible and safe String interpolation (Preview 🔍)
JDK 21var name = "Duke"; var info = STR."My name is \{name}"; -
Unnamed Classes and Instance Main Methods (Preview 🔍)
JDK 21// This is a complete and runnable program! void main() { System.out.println("Hello, World!"); } -
Sealed Classes can restrict which other classes may extend them
JDK 17(Preview 🔍 in JDK 16JDK 15)public abstract sealed class Shape permits Circle, Rectangle {...} public final class Circle extends Shape {...} // OK public final class Rectangle extends Shape {...} // OK public final class Triangle extends Shape {...} // Compile error // No need for default case if all permitted types are covered double area = switch (shape) { case Circle c -> Math.pow(c.radius(), 2) * Math.PI case Rectangle r -> r.a() * r.b() }; -
Record Classes, terse syntax to define immutable DTOs
JDK 16(Preview 🔍 in JDK 15JDK 14)record Point(int x, int y) { } var point = new Point(1, 2); point.x(); // returns 1 point.y(); // returns 2→ Related: Inside Java Podcast Episode 14 “Records Serialization” with Julia Boes and Chris Hegarty
-
Pattern Matching for
instanceofto eliminate the need for explicit casts after a type check
JDK 16(Preview 🔍 in JDK 15JDK 14)if (obj instanceof String s && s.length() > 5) { System.out.println("obj is a String with more than 5 characters: " + s.toUpperCase()); } -
Text Blocks
JDK 15(Preview 🔍 in JDK 14JDK 13)String html = """ <html> <body> <p>Hello, world</p> </body> </html> """; -
Helpful NullPointerExceptions describing precisely which variable was null
JDK 15(Enabled with-XX:+ShowCodeDetailsInExceptionMessagesin JDK 14)a.b.c.i = 99; --- Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException: Cannot read field "c" because "a.b" is null -
Switch Expressions
JDK 14(Preview 🔍 in JDK 12JDK 13)int numLetters = switch (day) { case MONDAY, FRIDAY, SUNDAY -> 6; case TUESDAY -> 7; default -> { String s = day.toString(); int result = s.length(); yield result; } }; -
Introduction of
varto make local variable declarations less ceremonious
JDK 11(Without lambda support in JDK 10)var greeting = "Hello World!"; -
Opt-in and backwards-compatible Module System to avoid
ClassDefNotFoundErrorsat runtime and create internal APIs
JDK 9(Project Jigsaw)module hu.advancedweb.helloworld { requires hu.advancedweb.somedependency; exports hu.advancedweb.hello } -
Private methods in interfaces
JDK 9(Milling Project Coin) -
Diamond operator for anonymous inner classes
JDK 9(Milling Project Coin) -
Try-with-resources allows effectively final variables
JDK 9(Milling Project Coin) -
@SafeVargson private instance methods
JDK 9(Milling Project Coin) -
No deprecation warnings on
importstatements
JDK 9
New APIs
Let's continue with the Java Standard Library, focusing on the new features that we can use in day-to-day coding.
If you are curious about all the API level differences between Java 8 later versions, check the AdoptOpenJDK/jdk-api-diff on GitHub or the The Java Version Almanac.
General
-
Sequenced Collections add interfaces to represent encounter order in collections, allowing, for example,
LinkedHashSetto serve as a substitute for aListand adding convenience methods likegetFirstandreverse
JDK 21void doSomething(SequencedCollection seq) { // ... } var set = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); var list = new ArrayList<String>(); doSomething(set); doSomething(list);→ Inside Java Podcast Episode 31 “Sequenced Collections” with Stuart Marks
-
Math.clampto fit the argument between min/max boundaries
JDK 21 -
StringBuffer.repeatandStringBuilder.repeat
JDK 21 -
splitWithDelimiterssplit variant forStringandPatternthat also returns the matching delimiters
JDK 21 -
BigInteger.parallelMultiply, an efficient and parallel implementation to multiply really huge numbers
JDK 19 -
BigDecimal.TWObecauseONEis not enough
(the real reason is to makeBigDecimalconsistent withBigInteger)
JDK 19 -
Math.divideExactforlongandintto perform a division and throw an exception if the result overflows
JDK 18 -
Java APIs that depend on the default charset will use UTF-8 by default
(e.g.InputStreamReader,FileReader,OutputStreamWriter,FileWriter,PrintStream,Formatter,Scanner)
If you need the old behavior check thefile.encodingand thenative.encodingsystem properties.
JDK 18
→ Related: Inside Java Podcast Episode 23 “Java 18 is Here” with Naoto Sato -
Service-provider interface for host name and address resolution, enabling mock resolvers in test scenarios and allowing frameworks to have finer control over resolution results
JDK 18 -
Vector API to express computations that compile to optimal hardware instructions (Incubator 🥚)
JDK 18JDK 17JDK 16 -
Foreign linker API for statically-typed, pure-Java access to native code (Incubator 🥚)
JDK 18JDK 17JDK 16 -
Foreign memory access API to access memory outside of the Java heap (Incubator 🥚)
JDK 18JDK 17JDK 16 -
Process::inputReader,Process::outputWritter,Process::errorReaderto access the standard input, output and error streams of the process
JDK 17 -
java.time.InstantSource, an interface that provides the current instant, an abstraction fromjava.time.Clockthat only focuses on the current instant and does not refer to the time zone
JDK 17 -
HexFormatto encode and decode of hexadecimal strings
JDK 17HexFormat.of().toHexDigits(123); // ==> "0000007b" HexFormat.of().fromHexDigits("0000007b"); // ==> 123 -
Align random generators (
Random,ThreadLocalRandom, andSplittableRandom) by providing common interfaces making it easier to use PRNG algorithms interchangeably, provide random Streams.
JDK 17new Random().ints() .limit(10) .forEach(System.out::println); -
Stream.toListas convenience for the most typical collection method (instead of relying on.collect(Collectors.toList()))
JDK 16List<String> result = Stream.of("one", "two", "three").stream() .filter(s -> s.length() == 3) .toList(); -
Stream.mapMultito replace each element of this stream with zero or more elements, an alternative toflatMap
JDK 16Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4) .mapMulti((number, downstream) -> downstream.accept(number)) .forEach(System.out::print); // prints 1234 -
New builder to HTTP client that specifies a header filter
JDK 16 -
DateTimeFormatterBuilder.html#appendDayPeriodTextto support other day periods than AM/PM
JDK 16 -
Unix-domain socket channels and server socket channels
JDK 16 -
@Serialto indicate fields and methods that are part of the serialization mechanism (e.g.serialVersionUIDandreadObject)
JDK 14 -
Support Non-Volatile Mapped Byte Buffers in the FileChannel API
JDK 14 -
Files.mismatch: find the first mismatched byte in the content of two files
JDK 12 -
Collectors.teeingto create a Collector that is a composite of two downstream collectors
JDK 12 -
String enhancements:
indentandtransform
JDK 12 -
Standard HTTP Client featuring HTTP/2, WebSocket support and non-blocking API
JDK 11(Incubator 🥚 in JDK 9)HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient.newBuilder().build(); HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder() .uri(URI.create("https://advancedweb.hu/")) .GET() .build(); HttpResponse<String> response = httpClient.send(request, BodyHandlers.ofString()); -
String enhancements, like
isBlank,lines,repeatandstrip
JDK 11 -
Convenience Factory Methods for Collections to ease the pain of not having collection literals
JDK 9Set<Integer> mySet = Set.of(1, 2, 3); List<Integer> myList = List.of(1, 2, 3); Map<String, Integer> myMap = Map.of("one", 1, "two", 2); -
Reactive Streams publish-subscribe framework for asynchronous stream processing with non-blocking backpressure
JDK 9 -
Time-based enhancements to
CompletableFuture(timeout, delay)
JDK 9 -
More options to transform (
dropWhile,takeWhile) and generate (iterate,ofNullable) streams; readonly collectors (toUnmodifiableList); optionals can be transformed to streams
JDK 9 -
Arrays.mismatch: find the first mismatching element between two arrays
JDK 9 -
System.LoggerAPI providing a common mechanism to handle platform logs, allowing JDK platform classes to use the same logging framework as the application
JDK 9 -
Stack-Walking API that allows laziness and stack-frame filtering
JDK 9 -
Process API provides more info and control (e.g. process ID, arguments, CPU time, parent/child processes), enhance
ProcessBuilderto aid the creation of process pipelines
JDK 9 -
VarHandleAPI to replace the field and array related operations ofjava.util.concurrent.atomicandsun.misc.Unsafein order to and provide low-level access mechamisms, e.g. atomic write.
JDK 9 -
New combinators and lookup methods for
MethodHandle
JDK 9 -
Enhanced Deprecation policy.
@Deprecatedcan be marked withforRemoval, which emits a new warning.
JDK 9 -
OASIS Standard XML Catalog API to manage external resources in XMLs in a secure and performant manner
JDK 9 -
Update JDK's XML parser, Xerces, to version 2.11.0
JDK 9 -
TIFF Support for Image I/O Framework
JDK 9
Internationalization
-
Unicode 10.0, adding roughly 27,000 characters, 10 blocks, and more than 30 scripts
JDK 11(Unicode 8.0 support in JDK 9) -
java.util.Localeand related APIs support currency type, time zone and more
JDK 10 -
ResourceBundleloads properties files in UTF-8 instead of ISO-8859-1
JDK 9 -
CLDR Locale Data Enabled by Default
JDK 9
Graphics and Desktop Applications
-
Desktop features for all platforms like login/logout/lock event listener and task bar interactions
JDK 9 -
MultiResolutionImagethat makes easy to retrieve a resolution-specific image for a DPI
JDK 9 -
HiDPI Graphics on Windows and Linux
JDK 9 -
Enable GTK 3 on Linux for JavaFX, Swing, and AWT
JDK 9 -
Replace
@beaninfoJavadoc tags with@BeanInfoannotations for Swing
JDK 9 -
Update GStreamer included in JavaFX/Media to version 1.4.4
JDK 9 -
Replace the existing ICU OpenType font-layout engine with HarfBuzz
JDK 9
Performance Improvements
General
-
Elastic metaspace to return unused HotSpot class-metadata memory to the operating system more promptly
JDK 16 -
Foreign-Memory Access API to safely and efficiently use off-heap memory (Incubator 🥚)
JDK 15JDK 14 -
Enable dynamic archiving of classes at the end of Java application execution
JDK 13 -
Class-Data Sharing archive of the default class list is enabled by default to improve out-of-the-box startup time
JDK 12 -
Application Class-Data Sharing to improve startup time and reduce footprint by sharing class metadata between Java processes.
JDK 10 -
Space-efficient, Compact Strings that stores Latin-1 only Strings more efficiently
JDK 9 -
Code caches of profiled and non-profiled compiled code is separated, resulting in improved performance and memory footprint
JDK 9 -
Store Interned Strings in Class-Data Sharing archives to reduce memory consumption
JDK 9
Library
-
New internal macOS rendering pipeline that supports Apple's new Metal Framework for the Java 2D API, replacing the old rendering pipeline that targets OpenGL which was deprecated by Apple in macOS 10.14
Performance comparision: JDK-8261408
JDK 17 -
Improved intrinsics for
java.lang.Mathsin,cosandlogfunctions on AArch64 processors
JDK 11 -
Security Manager performance improvements
JDK 9 -
Spin-Wait Hint (
Thread#onSpinWait) to optimize busy-waiting style loops
JDK 9 -
Use Marlin Renderer in Java 2D as the default graphics rasterizer instead of Pisces
JDK 9 -
Improved GHASH and RSA performance by leveraging recently-introduced SPARC and Intel x64 CPU instructions
JDK 9
Concurrency
-
Virtual Threads - lightweight user-mode threads that are cheap to create in huge numbers, making blocking APIs cool again
JDK 21(Preview 🔍 in JDK 20JDK 19)// With OS threads, this would be very problematic try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) { IntStream.range(0, 10_000).forEach(i -> { executor.submit(() -> { Thread.sleep(Duration.ofSeconds(1)); System.out.println("" + i); return i; }); }); }→ Virtual Threads: An Adoption Guide - Oracle
→ Inside Java Podcast Episode 29 “Helidon Níma & Virtual Threads” with Tomas Langer -
Structured concurrency API (Preview 🔍) to define subtask relations between threads to streamline error handling and cancellation, improve reliability, and enhance observability
JDK 21(Incubator 🥚 in JDK 20JDK 19)try (var scope = new StructuredTaskScope.ShutdownOnFailure()) { Supplier<String> user = scope.fork(() -> findUser()); Supplier<Integer> order = scope.fork(() -> fetchOrder()); scope.join() // Join both subtasks .throwIfFailed(); // ... and propagate errors // Here, both subtasks have succeeded, so compose their results return new Response(user.get(), order.get()); } -
Scoped Values (Preview 🔍), an alternative to ThreadLocal that allows sharing immutable data with limit visibility
JDK 21(Incubator 🥚 in JDK 20) -
Thread-Local Handshakes to stop individual threads
JDK 10 -
Improved performance of contended object monitors
JDK 9 -
Extra space on thread stack for critical sections, mitigating the risk of a deadlock in
java.util.concurrentlocks in case of a stack overflow
JDK 9
Native access
-
Foreign Function & Memory API (Preview 🔍), alternative to JNI to access native code and memory with a safe, pure Java API
JDK 21JDK 20JDK 19(Incubator 🥚 in JDK 18JDK 17)import java.lang.foreign.*; import java.lang.invoke.*; Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker(); SymbolLookup stdlib = linker.defaultLookup(); MethodHandle strlen = linker.downcallHandle( stdlib.find("strlen").get(), FunctionDescriptor.of(ValueLayout.JAVA_LONG, ValueLayout.ADDRESS) ); try (Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) { MemorySegment cString = arena.allocateUtf8String("Hello"); long len = (long)strlen.invoke(cString); System.out.println("Length: " + len); }→ Project Panama - Foreign Function & Memory API - JVMLS 2023
-
Vector API (Incubator 🥚) for efficient vector operations, e.g. for ML workloads
JDK 21JDK 20JDK 19JDK 18JDK 17JDK 16
Compiler
-
Java based JVM compiler interface (JVMCI) (Experimental 💥)
JDK 9(JVM Compiler Interface) -
Performance improvement in javac: new strategy for type checking poly expressions
JDK 9
G1 Garbage Collector (default)
-
Configurable Card Table Card Size (
-XX:GCCardSizeInBytes)
JDK 18 -
Allow G1 Heap Regions up to 512MB
JDK 18 -
NUMA-Aware Memory Allocation
JDK 14 -
Abortable mixed collections to meet user-supplied pause goals
JDK 12 -
Automatically return heap memory to the operating system when idle
JDK 12 -
Parallel Full GC to improve worst-case latencies
JDK 10 -
G1 Garbage Collector is now the default instead of Parallel GC
JDK 9
Other Garbage Collectors
-
Generational ZGC
JDK 21→ Inside Java Podcast Episode 24 “Towards Generational ZGC!” with Erik Österlund
-
Configurable Card Table Card Size (
-XX:GCCardSizeInBytes) for Serial and Parallel GC
JDK 18 -
SerialGC, ParallelGC and ZGC now supports String Deduplication
JDK 18JDK 18JDK 18 -
Z Garbage Collector, offering very low pause times on large heaps
JDK 16JDK 15(Experimental 💥 in JDK 14{.label-java-14} (Windows) JDK 14{.label-java-14} (OS X) JDK 11{.label-java-11} (Linux) ) -
Shenandoah Garbage Collector, offering similar benefits as ZGC but based on a different algorithm
JDK 15(Experimental 💥 in JDK 12) -
Epsilon Garbage Collector, which does not implement actual memory reclamation, striving for the lowest overhead possible
JDK 11 -
XX:AllocateHeapAt=<path>to support Alternative Memory Devices
JDK 10
Diagnostic and Tools
-
Flight Recorder Event Streaming: profiling data is available via an API, making it suitable for continuous monitoring
JDK 14 -
Microbenchmark Suite based on JMH
JDK 12 -
Flight Recorder is part of OpenJDK
JDK 11 -
Low-Overhead Heap Profiling via JMTI
JDK 11 -
Run-time manageable and method specific control of the C1 and C2 compilers that enables contained tests
JDK 9 -
Fine-grained, easy-to-configure Logging System for all components of the JVM
JDK 9(Unified JVM Logging) JDK 9(Unified GC Logging) -
Allow the application to provide logger implementation to be used by platform classes
JDK 9
Security Improvements
-
Key Encapsulation Mechanisms (KEMs) API
JDK 21 -
The
cacertskeystore file is now a passwordlessPKCS12file
JDK 18 -
Calling
keyStore.store(outputStream, null)on aPKCS12KeyStore creates a passwordlessPKCS12file
JDK 18 -
Default set of root Certification Authority (CA) certificates are provided with the JDK, so TLS connections are working out of the box
JDK 10 -
Default keystore type is the standard PKCS12 instead of the proprietary JKS
JDK 9 -
DRBG-Based
SecureRandom
JDK 9 -
Disable X.509 certificate chains with SHA-1 based signatures
JDK 9 -
SHA-3 Hash Algorithms
JDK 9
TLS
-
TLS 1.3 support
JDK 11 -
API for Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)
JDK 9 -
OCSP stapling TLS to improve performance of certificate status checking
JDK 9 -
TLS Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation (ALPN) Extension which enables protocol negotiation without additional round trips; ALPN is a requirement for HTTP/2 connections
JDK 9
Crypto
-
Edwards-Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (EdDSA) - RFC8032
JDK 15 -
Key Agreement with Curve25519 and Curve448
JDK 11 -
ChaCha20 and Poly1305 Cryptographic Algorithms
JDK 11
Launching
-
jwebservercommand line utility to serve static files
(similar to Python'sSimpleHTTPServer, for development and education purposes)
JDK 18
→ Related: Inside Java Podcast Episode 22 “Simple Web Server” with Julia Boes -
Launch Single-File Source-Code Programs, including support for shebang (
#!) line on Unix
JDK 11 -
jshell: the Java REPL
JDK 9(Project Kulla)
→ Related: Prototyping with JShellRelatedExploring REPL-driven development in JShell -
Compile for Older Platform Versions with
--release, which configures--sourceand--targetand links against the appropriate platform version
JDK 9 -
Early validatation of JVM Command-Line Flags to avoid crashes
JDK 9
Packaging
-
javacnow assumes that source files are encoded with the new default UTF-8 charset
(In previous versions of Java, developers were strongly encouraged to pin the charset to UTF-8 when compiling, that's no longer needed.)
JDK 18 -
Packaging Tool to create self-contained applications, also supporting native package formats: msi, exe, pkg, dmg, deb and rpm
JDK 16(Incubator 🥚 in JDK 14)
→ Related: Inside Java Podcast Episode 12 “jpackage” with Kevin Rushforth -
jlinkJava Linker that can build an optimized, slim run-time image for a modular Java application that contains only the required parts of the JDK
JDK 9- [2], [3], [4], [4], [5] -
Multi-Release JAR Files to allow multiple, Java-release-specific versions of class in a single archive
JDK 9
Javadoc
-
@snippettag, a modern alternative for@codethat supports multi-line code, supports styling and the inclusion of external snippets
JDK 18Example for an internal snippet:
/** * Highlighting based on regex: * {@snippet : * if (v.isPresent()) { * System.out.println("Hello, World!"); // @highlight regex='".*"' * } *} */ public void myMethod() { // ... }Example for an external snippet:
/** * {@snippet class="ch.adnovum.Example" region="optional" } */ public void myMethod() { // ... } public void exampleSnippetCode() { var v = Optional.empty(); // @start region=optional if (v.isPresent()) { System.out.println("v: " + v.get()); } // @end region=optional }→ Related: Programmer's Guide to Snippets - Jonathan Gibbons, Pavel Rappo
→ Related: Configuring Maven For Compiled And Tested Code In Javadoc - Nicolai Parlog -
The Javadoc tool now emits HTML5 markup instead of a frame-based layout and the documentation contains a search box to ease navigation
JDK 9- [2], [3]
Bytecode
-
Replace
Unsafe::defineAnonymousClass()withLookup::defineHiddenClass(), intended for frameworks to dynamically generate Hidden Classes that can't be discovered, linked, and used directly by other classes. JDK 15 -
java.lang.invoke.constantpackage to allow easy description of loadable constants (operands for theldcinstruction), which is less error-prone than relying on ad-hoc String representation
JDK 12 -
CONSTANT_Dynamicconstant-pool entry which uses bootstrapping to perform the resolution, similarly toINVOKEDYNAMICcalls
JDK 11 -
Introduction of the Nest access-control context that wraps classes in the same code entity - such as nested classes - and eliminates the need for compiler to insert bridge methods to the generated bytecode.
JDK 11 -
Bytecode generated for static String-concatenation uses
invokedynamicrather than directly creatingStringBuilder#appendchains. This will enable future optimizations of String concatenation without requiring bytecode changes.
JDK 9 -
INVOKEDYNAMICcan express high-level operations on object properties and or collections
JDK 9
New supported platforms
-
Linux/RISC-V
JDK 19 -
macOS/AArch64
JDK 17 -
Alpine
JDK 16 -
Windows/AArch64
JDK 16 -
Linux/AArch64
JDK 9 -
Linux/s390x
JDK 9 -
Unified arm32/arm64
JDK 9
New Version Scheme
Deprecation and removal
-
Deprecate the Windows 32-bit x86 Port for Removal
Windows 10, the last Windows operating system to support 32-bit operation, will reach End of Life in October 2025
JDK 21 -
Prepare to Disallow the Dynamic Loading of Agents to improve the integrity and security of the platform
JDK 21Since JDK 9 the dynamic loading of agents can be disallowed with the
-XX:-EnableDynamicAgentLoading, but is enabled by default.
In JDK 21, it is allowed but the JVM issues a warning when it occurs. For example:WARNING: A {Java,JVM TI} agent has been loaded dynamically (file:/u/bob/agent.jar) WARNING: If a serviceability tool is in use, please run with -XX:+EnableDynamicAgentLoading to hide this warning WARNING: If a serviceability tool is not in use, please run with -Djdk.instrument.traceUsage for more information WARNING: Dynamic loading of agents will be disallowed by default in a future releaseIn some future release, the dynamic loading of agents will be disallowed by default.
Some tools might rely on dynamic loading of agents, so watch out for these warnings.
Note: it is not a goal to prevent agents from being loaded at startup via the-javaagentor-agentlibcommand-line options. Also, the Attach API which is uesed by serviceability tools to connect to a running JVM instance is not affected. -
Deprecate
java.net.URLconstructors. Developers are encouraged to usejava.net.URIto parse or construct a URLs, becausejava.net.URL(dating from the first version of Java) does not perform any URL encoding/decoding. → Quality Outreach Heads-up - JDK 20: Deprecate URL Public Constructors -
Deprecate Finalization for removal
JDK 18(Deprecated in JDK 9)Overriding the finalize method is a way to involve the GC to release resources when a corresponding object is garbage collected.
Because memory management and resource management are different issues this coupling creates some problems, such as unpredictable latency (the finalizer might be called much later), threading issues (finalizers run on their own threads, possibly making a single-threaded program accidentally multi-threaded), performance (even if you don't rely on finalizers, you can't opt-out), and hard to troubleshoot scenarios (exceptions in finalizers are ignored).For better alternatives, consider
try-with-resourcesand the Cleaner API. Check the JDK Flight Recorder Event for Finalization and the--finalization=disabledcommand-line option to see if your codebase is relying on finalizers.→ Related: Inside Java Podcast Episode 21 “JEP 421 and Finalization Deprecation” with Brent Christian
→ Related: What Happens to Finalization in JDK 18? - Inside Java Newscast #15 -
Deprecate
Thread.stopfor removal
JDK 18(Deprecated in Java 1.2) -
JARs signed with SHA-1 algorithms are now restricted by default and treated as if they were unsigned
JDK 18 -
Strongly encapsulate internal API's (
sun.*) except for critical APIs such assun.misc.Unsafe.
Remove the option for relaxed strong encapsulation via the--illegal-accesslauncher option
JDK 17(Strong encapsulation is the default in JDK 16with the ability to opt-out with--illegal-access,
Relaxed strong encapsulation (--illegal-access=permit) is the default in JDK 9- [2] that warns on the first illegal reflective-access operation.)
→ Related: Inside Java Podcast Episode 18 “Java's steady march towards strong encapsulation” with Alan Bateman -
Make floating-point operations consistently strict by default, warn when the
strictfpmodifier is used
JDK 17
→ Related: Wikipedia article explaining whatstrictfp -
Remove RMI Activation, affecting the
java.rmi.activationpackage and thermidtool, does not affect Java RMI in general
JDK 17(Deprecated in JDK 15) -
Deprecate Applet API (
java.applet.*,javax.swing.JAppletandjava.beans.AppletInitializer) for removal
JDK 17(Deprecated in JDK 9) -
Deprecate the Security Manager for Removal
Work ongoing to consider use cases where the Security Manager is useful and provide alternatives (e.g. JDK-8199704)
JDK 17 -
Remove the Experimental AOT and JIT compiler due to lack of interest.
JDK 17 -
Deprecate the constructors of primitive wrapper classes, disallow synchronization on wrapper objects
(Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Float,Double,Boolean, andCharacter)
JDK 16 -
Remove the Nashorn Javascript Engine and the
jjstool
JDK 15(Deprecated in JDK 11) -
Remove the Solaris and SPARC Ports
JDK 15(Deprecated in JDK 14) -
Disable Biased Locking by default, deprecate related command-line flags
JDK 15 -
Deprecate
Unsafe::defineAnonymousClass()
JDK 15 -
Remove the Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) Garbage Collector
JDK 14 -
Deprecate the ParallelScavenge + SerialOld GC Combination
JDK 14 -
Remove the Pack200 Tools and API
JDK 14 -
Deprecate the Pack200 Tools and API
JDK 11 -
Remove Java EE
JDK 11 -
Remove CORBA
JDK 11 -
Remove
Thread.destroy()andThread.stop(Throwable)
JDK 11 -
varis no longer a valid class name
JDK 10 -
Remove the javah tool
JDK 10 -
Underscore is no longer a valid identifier
JDK 9 -
Remove
apple.applescriptandcom.applepackages
JDK 9 -
Disable X.509 certificate chains with SHA-1 based signatures
JDK 9 -
Remove Launch-Time JRE Version Selection directives:
JRE-Versionmanifest entry and-version:cli option
JDK 9 -
Remove the jhat tool
JDK 9 -
Remove the JVM TI hprof Agent
JDK 9 -
Remove GC Combinations Deprecated in JDK 8
JDK 9 -
Deprecate the Concurrent Mark Sweep Garbage Collector
JDK 9 -
Remove the Endorsed Standards Override (
lib/endorsed) and Extensions (lib/ext) mechanisms from the JRE
JDK 9 -
Remove
rt.jarfrom the JRE
JDK 9
If you are curious about all the API level differences between Java 8 and 14, check the Java Almanac project. Also check out jdeps, the Java class dependency analyzer to find out if your project is still using an old internal API.
Summary
JDK 8 was released in 2014. We had to wait for three and a half years for JDK 9. But since then things accelerated. Java has a new release structure that aims to deliver a new version in every six months.
While Java 8 is still supported, migrating to the latest version brings considerable amount of improvements to the table.




